Wood as a Raw Material
Ever Increasing Sustainability
Wood is a renewable resource which is available in large quantities and offers the most varied types of application.
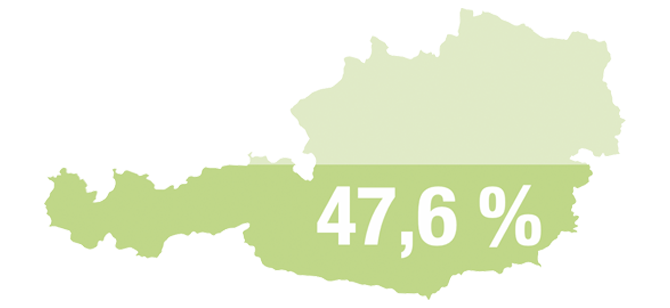
A Country of Forests
There are 4 million hectares of forest in Austria - this corresponds to 47,6 % of the total surface area. 1.1 billion m³ of wood is available for use from the Austrian forest.
In addition, 31 million m³ of wood is regenerated every year, of which only two thirds are used.
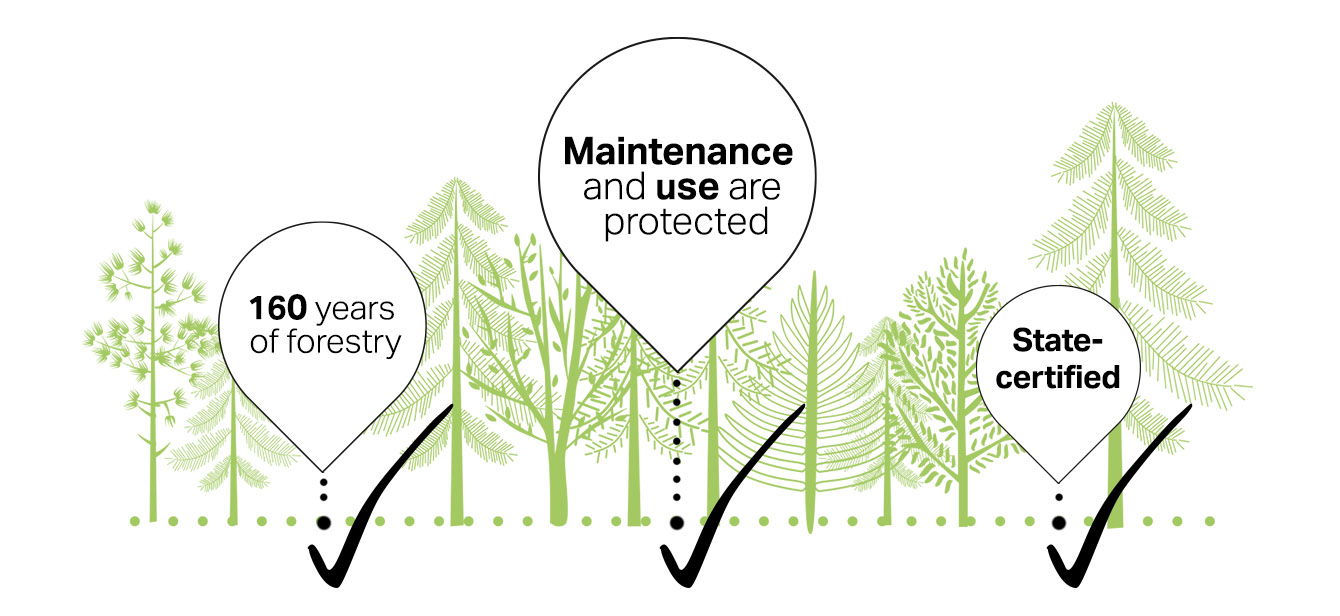
Taking and Giving Back
Austria’s forestry sector has been governed by some of the world’s strictest forestry laws for 160 years. When maintaining and using the forests, it is important to ensure that their biodiversity, productivity, and capacity for regeneration are preserved, both now and for the future. Austria is the only EU country to require forest owners with a minimum forest area of 1000 hectares to employ full-time state-certified foresters.
PEFC certified
PEFC, the world’s largest forest certification system is now more than 20 years old.
As a PEFC-certified company, we are proud to be part of this success story and look forward to the coming years in which we will continue to work together on ensuring sustainable, climate-fit forestry in the earth’s forests.

Climate-friendly
Wood is one of the most important natural stores of CO2.
Forests are not only important for recreational use and for the timber they produce but they make a significant contribution to climate protection.
Trees extract the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air as they grow. The carbon remains stored in the trees, while the oxygen is released back into the atmosphere.
If the wood is not used, the carbon dioxide is released back into the environment when the tree decomposes in the forest. By using timber products as a construction material, this carbon dioxide can remain stored in the wood for decades, which helps to reduce CO2 emissions.
800 million tonnes of carbon (CO2) are stored in Austria’s forests.
That corresponds to approx. 3 billion tonnes of bound CO2 or 35 times the amount of CO2 that is emitted in Austria each year.

Mosser – climate formula
Wood used for construction binds CO2, thereby reducing the impact on our climate.
The quantity of wood we process each day binds a volume of CO2 equal to the weight of 333 hippos for an extended period of time.
Eco to the end
At the end of its life cycle, wood does not need costly disposal.
By recycling or upcycling, e.g. new furniture made from old roof trusses.
When raw materials can no longer be used, wood can be burnt & used to generate energy.
This means at the end, only as much CO2 is emitted as was bound at the start of photosynthesis.
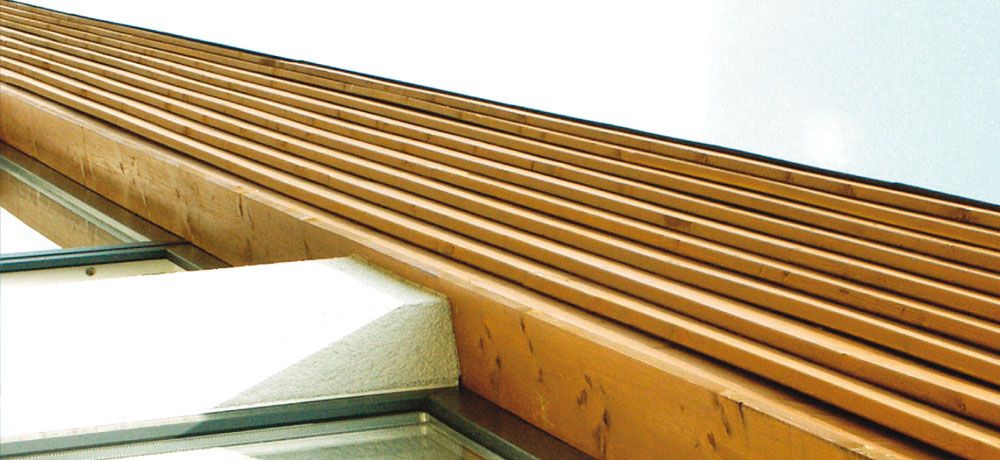
Construction with Wood

Wood is light but sturdy and is therefore extremely versatile in its application - a high performance material from nature with different degrees of strength and rigidity.
Modern wood products have optimized construction and static properties.
The practically unlimited possibilities of shaping wood make it possible to produce elegant and extraordinary constructions.
As wood absorbs water and is breathable, it provides a pleasant room climate the whole year round.
Wood is electrostatic neutral and non-conductive.
Due to its low heat conductivity, wood possesses very good insulating properties.
The heat insulation provided by a thin 10 cm solid wooden wall is equivalent to that of a concrete wall 160 cm thick. Even at a relatively low ambient temperature a wooden surface feels pleasantly warm.
Wood may become wet, but it must be able to dry again. If this is taken into account then wood will last for an almost unlimited period.

Construction with wood reduces the ecological footprint
Harvesting wood from the forest and using it as a building material increases the forest’s climate protection.
Every cubic meter of wood used for construction binds a tonne of CO2 for the long term.
At the same time, new trees are growing in the forest in place of the felled trees, and these again actively absorb CO2.
Over their entire life cycle, wooden buildings have a 50% lower CO2 footprint than buildings made of non-renewable materials.
Wood can therefore help slow the rise of CO2 in the atmosphere and is a proven weapon in the fight against climate change.
Products made from wood use substantially less energy during their production than, for example, steel, plastic or concrete. Accordingly, these resources are conserved through the use of wood.

An average family house built using wood construction requires around 40 cubic meters of wood. This means that the wood required for 2160 houses can be grown in just one day.
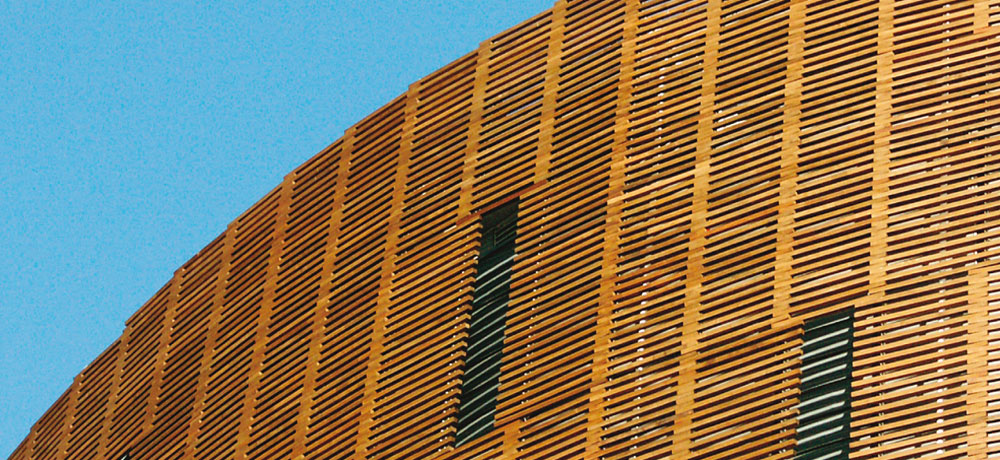
Taller—more individual—more spectacular
Modern wood construction is currently experiencing a real boom thanks to its versatile and positive properties and the enormous potential for development.
Wood is now increasingly being used as a construction material in urban areas too as well as in multi-story buildings.

The great adaptability of wood as a construction material means that there are no limits on the architect’s imagination.
The Important Economic Role of Wood

Austria’s forests support 300,000 livelihoods
The wood industry is an important sector of the economy and one of Austria’s largest employers.
The renewable raw material of wood safeguards around 300,000 jobs along the value chain.
The raw material of wood safeguards jobs in rural areas
Forestry is by far the biggest investor in rural areas.
It creates jobs in the countryside and in structurally weak regions.
An important contribution to national value creation
Companies from the timber industry together generate a production value of EUR 12 billion a year.
Measured in terms of the export surplus, forestry is the second biggest sector of the economy.
In some areas, forestry is even the global market leader.






